Bitcoin, Money, and the S-Curve: A Path to Multi-Million Dollar Valuation
- Four Dimensional Partners

- Jan 5, 2025
- 9 min read
Introduction: The Next Evolution in Money
Throughout history, societies have converged on a single monetary standard, from gold to fiat currencies, driven by the need for efficiency, trust, and network effects. Today, Bitcoin stands as the most compelling contender to dominate this role in the digital age.
For investors, Bitcoin represents more than a speculative asset—it’s an opportunity to own a stake in what could become the foundation of the global financial system. By understanding Bitcoin’s adoption trajectory through the lens of the S-curve and its relation to the $900 trillion global asset market, one can grasp its transformative potential—and the future value it could command.

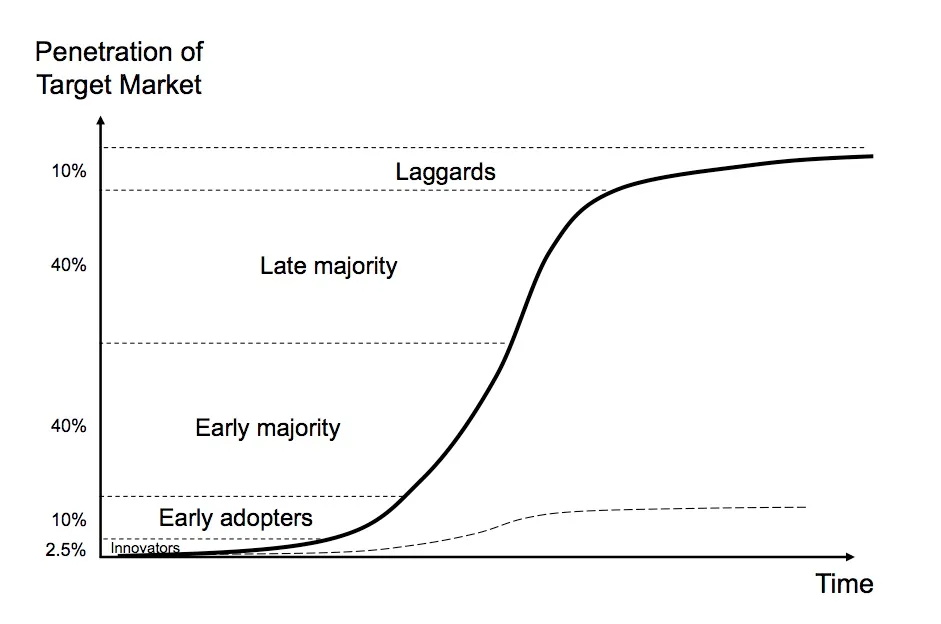
The S-Curve of Adoption: Bitcoin’s Roadmap
The S-curve provides a roadmap for how Bitcoin could grow into its role as the global monetary standard:
Early Stage (2009–2016): Slow growth as Bitcoin was adopted by enthusiasts and innovators.
Acceleration Phase (2017–Present): Rapid adoption driven by institutional interest, global financial uncertainty, and increasing trust in Bitcoin as a store of value.
Maturity Phase (Future): Bitcoin could achieve broad adoption as a global reserve asset and neutral settlement layer, reflecting its role as "rules without rulers."
Unlike consumer technologies, Bitcoin is money, and money systems historically operate under winner-take-all dynamics. Societies converge on a single dominant monetary standard because it simplifies transactions, minimizes friction, and builds trust across borders.
Why Bitcoin Fits the S-Curve with Parabolic Adoption
Bitcoin’s adoption aligns with the S-curve—a proven model for technological growth—marked by slow early adoption, rapid acceleration, and eventual maturity. Its unique properties as a monetary network, combined with historical parallels and global economic trends, position Bitcoin for exponential, parabolic growth.
1. A Revolutionary Technology with Network Effects
Disruptive Innovation: Bitcoin introduces a trustless, decentralized monetary system, solving inefficiencies in fiat currencies and gold.
Exponential Growth: Like the internet and mobile phones, Bitcoin’s value grows as more participants join the network, creating powerful network effects.
Adoption Trajectory: Early adopters (cypherpunks, technologists) gave way to institutional treasuries and governments, accelerating its rise.
2. Unique Properties Driving Parabolic Growth
Bitcoin’s characteristics make it uniquely suited for exponential adoption:
Scarcity: A fixed supply of 21 million coins ensures demand drives value.
Censorship Resistance: Decentralized design protects against interference, attracting users in politically unstable regions.
Borderless Utility: Accessible globally, Bitcoin transcends geographical and socioeconomic boundaries.
3. Historical Parallels with Technology Adoption
The Internet: Slow early growth (1970s–1990s) led to rapid mainstream adoption, mirroring Bitcoin’s trajectory.
Mobile Phones: Initial high costs and limited infrastructure were overcome by network effects and scaling, as seen with Bitcoin’s improved wallets and Lightning Network.
4. Economic Trends Accelerating Bitcoin
Inflation Hedge: Currency debasement and inflation push adoption in emerging markets and developed economies alike.
Institutional Legitimacy: Companies like MicroStrategy and governments like El Salvador validate Bitcoin as a global store of value.
Evolving Infrastructure: Custody solutions, secure wallets, and payment systems enable seamless global adoption.
Bitcoin’s adoption perfectly fits the S-curve model, driven by its revolutionary nature, unique properties, and accelerating global trends. As it follows this trajectory, Bitcoin is poised for parabolic growth, reshaping the global financial system.
The TAM for Bitcoin: Breaking Down the $900 Trillion Total Addressable Market
Bitcoin’s potential is best understood in the context of the total addressable market (TAM) for global assets, which encompasses the vast spectrum of wealth storage systems in the global economy. This includes major asset classes such as gold, real estate, bonds, equities, and fiat currencies, all of which are used to preserve and grow wealth. Collectively, these markets represent an estimated $900 trillion in global value, highlighting the scale of the opportunity.
Bitcoin’s unique properties—unmatched portability, absolute scarcity, and decentralized design—position it as a superior alternative to legacy wealth storage systems. Unlike traditional assets that are often hindered by inefficiencies, geographic limitations, and systemic risks, Bitcoin offers a modern, efficient, and borderless solution, enabling it to capture significant shares of these markets.
As Bitcoin adoption grows, its superior qualities as a store of value make it increasingly attractive compared to traditional options like real estate, gold, and bonds. This shift will accelerate over time, with Bitcoin progressively absorbing market share from these assets as individuals and institutions recognize its ability to preserve and grow wealth more effectively.
Let's take a look at Bitcoin VS global assets illustrated in the chart below:

Gold ($16 Trillion):
Gold has served as a store of value for millennia, but Bitcoin’s superior portability, divisibility, and resistance to confiscation make it a natural successor.
Real Estate ($330 Trillion):
Real estate is often used as a store of value but is illiquid, expensive to maintain, and geographically tied. Bitcoin offers a superior alternative as a global, liquid, and maintenance-free store of value.
Bonds ($300 Trillion):
Bonds are becoming less attractive as real yields turn negative. Bitcoin’s deflationary nature and long-term appreciation potential make it a compelling alternative.
Equities ($115 Trillion):
Equities represent productive enterprises but are inherently tied to economic cycles. Bitcoin offers neutrality as a non-sovereign store of value, making it an attractive hedge during market instability.
Money ($120 Trillion):
Bitcoin’s censorship resistance and global accessibility position it to replace a significant share of fiat money, especially in inflationary economies.
Bitcoin’s Price in the Context of the TAM for Money
Bitcoin’s fixed supply of 21 million coins ensures that as demand increases, its price must rise due to its inelastic supply dynamics. Unlike fiat currencies or commodities like gold, Bitcoin’s supply is permanently capped and cannot expand to meet rising demand.
This inelasticity is reinforced by Bitcoin’s halving process, which reduces new issuance every four years, creating periodic supply shocks. As institutions, individuals, and governments adopt Bitcoin as a hedge or store of value, the limited supply drives significant price appreciation, with demand being the sole balancing mechanism.
Unlike commodities that can increase production in response to price, Bitcoin’s immutable supply creates a purely demand-driven market, positioning it as a deflationary asset whose value grows with adoption. This dynamic ensures Bitcoin’s long-term appreciation as a premier store of value.
Here’s what the numbers look like in three adoption scenarios of different degrees:
Tier 1: Modest Adoption (Conservative Growth)
Bitcoin complements existing asset classes but doesn’t fully replace them.
Market | Market Share Captured | Market Cap ($T) | Bitcoin Price ($) |
Gold | 100% | $16T | ~$761,900 |
Real Estate | 10% | $33T | ~$1.57M |
Bonds | 10% | $30T | ~$1.42M |
Equities | 5% | $5.75T | ~$273,800 |
Money | 10% | $12T | ~$571,400 |
Total Market Cap: $96.75T
Bitcoin Price: ~$4.6M per coin
Tier 2: Significant Adoption (Aggressive Growth)
Bitcoin becomes the preferred store of value for investors seeking simplicity, security, and global accessibility.
Market | Market Share Captured | Market Cap ($T) | Bitcoin Price ($) |
Gold | 100% | $16T | ~$761,900 |
Real Estate | 25% | $82.5T | ~$3.93M |
Bonds | 20% | $60T | ~$2.85M |
Equities | 10% | $11.5T | ~$547,600 |
Money | 25% | $30T | ~$1.42M |
Total Market Cap: $200T
Bitcoin Price: ~$9.5M per coin
Tier 3: Dominant Adoption (Bitcoin as Global Standard)
Bitcoin becomes the primary global store of value, replacing inefficient assets like real estate and bonds while capturing massive shares of the equity and money markets.
Market | Market Share Captured | Market Cap ($T) | Bitcoin Price ($) |
Gold | 100% | $16T | ~$761,900 |
Real Estate | 50% | $165T | ~$7.85M |
Bonds | 50% | $150T | ~$7.14M |
Equities | 20% | $23T | ~$1.09M |
Money | 50% | $60T | ~$2.85M |
Total Market Cap: $414T
Bitcoin Price: ~$19.7M per coin
Why Bitcoin Could Dominate Traditional Asset Classes
1. Real Estate as a Store of Value
Real estate has long been a preferred store of value for investors, but it comes with significant drawbacks:
Illiquidity: Real estate transactions are complex, expensive, and slow. Selling or acquiring property can take weeks or months, limiting its flexibility as a liquid asset. Bitcoin, on the other hand, can be transferred globally within minutes, providing unparalleled liquidity.
Maintenance Costs: Owning real estate involves ongoing expenses such as property taxes, insurance, and maintenance. These costs can erode long-term returns, especially in markets where property appreciation is slow. Bitcoin has no associated carrying costs, making it a more efficient wealth storage option.
Government Interference: Real estate is often subject to local regulations, eminent domain risks, and geopolitical instability. In contrast, Bitcoin is decentralized and immune to government seizure, making it a more secure and reliable store of wealth.
Scalability: Unlike real estate, which is limited by geography and physical constraints, Bitcoin is borderless and infinitely divisible, making it accessible to anyone, anywhere.
2. Gold’s Limitations
Gold has been the standard store of value for millennia, but it is increasingly losing relevance in the digital age:
Physicality as a Liability: Gold is cumbersome to store, difficult to transport, and expensive to secure. Bitcoin, being digital, eliminates these issues entirely. It can be stored securely with cryptographic keys and transferred globally without intermediaries.
Fixed Supply: While gold’s supply increases modestly through mining, Bitcoin’s supply is capped at 21 million coins. This hard cap ensures absolute scarcity, which is critical for preserving value over time.
Borderless Nature: Gold is tied to physical locations, making it vulnerable to confiscation or geopolitical restrictions. Bitcoin’s decentralized network allows it to exist and operate independently of national borders or centralized control.
Superior Divisibility: Bitcoin can be divided into units as small as a satoshi (1/100,000,000 of a Bitcoin), enabling microtransactions and accessibility for all levels of investment, unlike gold, which is limited in this regard.
3. Bonds and Equities
While bonds and equities have been staples of traditional investment portfolios, Bitcoin offers distinct advantages:
Deflationary Growth: Bonds, particularly in low-interest-rate environments, often provide negative real yields, eroding investor wealth over time. Bitcoin’s deflationary nature, due to its fixed supply and increasing demand, offers a more attractive long-term growth profile.
Neutrality: Equities are tied to specific companies, industries, and economic cycles, making them inherently volatile and susceptible to macroeconomic shocks. Bitcoin operates outside these cycles as a neutral, global asset, providing stability and diversification.
Risk Hedging: Bonds and equities are vulnerable to systemic risks, including inflation, monetary policy changes, and geopolitical events. Bitcoin’s decentralized design insulates it from these risks, making it a compelling hedge.
Accessibility: Bitcoin can be accessed, traded, and secured globally without intermediaries, whereas bonds and equities typically require brokers, custodians, and market access.
4. Money
Bitcoin’s ability to function as rules without rulers positions it as the ultimate global settlement layer:
Censorship Resistance: Bitcoin transactions cannot be blocked or reversed by governments or financial institutions, making it ideal for cross-border payments and settlements.
Neutral Infrastructure: Unlike fiat money, which is controlled by central banks and subject to inflationary policies, Bitcoin operates on a decentralized network with transparent, immutable rules. This ensures trust and predictability for all participants.
Portability: Traditional forms of money, such as cash or bank transfers, are limited by borders, banking hours, and intermediary systems like SWIFT. Bitcoin is accessible 24/7 and can be transferred anywhere in the world instantly.
Programmability: Bitcoin’s blockchain enables programmable money, allowing for complex financial contracts, escrow arrangements, and other innovations to be executed seamlessly. This capability extends its utility far beyond that of traditional currencies.
Global Standardization: As Bitcoin adoption grows, its universal nature could make it the standard unit of account for global trade, reducing inefficiencies caused by currency exchange rates and fiat volatility.
Conclusion: Bitcoin’s Inevitable Rise to Global Dominance
Bitcoin is not just another asset—it is a monetary revolution, fundamentally transforming how value is stored, transferred, and trusted across the globe. As the first decentralized digital money, Bitcoin operates outside the control of governments, central banks, or institutions. Its inherent scarcity, unmatched portability, and ability to function as rules without rulers make it uniquely suited to thrive in the modern, interconnected economy.
With a Total Addressable Market (TAM) of $900 trillion, Bitcoin’s potential market cap dwarfs its current valuation. This TAM includes global wealth, gold, real estate, bonds, equities, and fiat money—markets that are ripe for disruption by a more efficient and resilient store of value. Bitcoin’s design enables it to replace or complement these traditional asset classes, positioning it to absorb significant portions of global wealth.
Even under modest adoption scenarios, where Bitcoin captures only a fraction of the TAM, its price could reach $4.6 million per coin. In more aggressive adoption scenarios, where Bitcoin becomes the preferred store of value for investors worldwide, its price could exceed $9.5 million per coin. And in the most transformative outcome, where Bitcoin emerges as the primary global store of value and monetary standard, its price could surpass $19.7 million per coin—reflecting its role in securing and transacting the wealth of the world.
The Case for Action
The question is no longer whether Bitcoin will dominate but rather how much of the global economy it will transform—and how soon. History has shown that monetary revolutions are not gradual but exponential. Gold’s rise as a universal standard, the U.S. dollar’s ascent as the global reserve currency, and the rapid adoption of the internet are all examples of how network effects accelerate transitions to superior systems.
For family offices and institutional investors, this represents a once-in-a-generation opportunity. Early participation in Bitcoin’s rise offers asymmetric upside potential, securing a stake in what could become the foundation of the future financial system. The cost of delay is missing out on a revolution that will define the 21st century.
A Monetary Transformation in Progress
Bitcoin’s rise is not just a story of price appreciation; it is the emergence of a new monetary paradigm. By enabling trustless, borderless, and censorship-resistant transactions, Bitcoin democratizes access to the global economy. It eliminates inefficiencies inherent in traditional systems and provides a framework for storing and transferring value that is robust, equitable, and incorruptible.
The time to act is now. Bitcoin’s trajectory along the S-curve of adoption is accelerating, and its ascent to dominance is inevitable. For those with the vision to see its potential, Bitcoin is not just an investment—it is a gateway to the financial system of the future. The opportunity to be a part of this transformation is unprecedented. Don’t miss it.






Comments